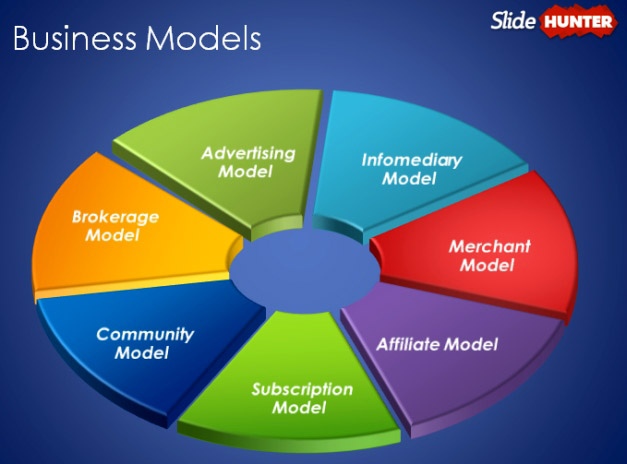
The term “startup” has become synonymous with innovation, agility, and disruption in the business world. But what exactly defines a startup, and how does it distinguish itself from more established, traditional companies? This article delves into the essence of startups and explores the key distinctions that set them apart from their more conventional counterparts.
Defining a Startup: A startup is a company that is in the early stages of its development, typically characterized by a focus on innovation, scalability, and the pursuit of a unique business model. Unlike traditional companies that may have established products, customer bases, and stable revenue streams, startups are often characterized by their dynamic and experimental nature.
Key Differences Between Startups and Traditional Companies:
- Innovation and Disruption:
- Startups: Innovation is at the core of a startup’s DNA. Startups often enter the market with groundbreaking ideas or solutions that challenge existing norms and practices. Disruption is a common goal, aiming to introduce something new or more efficient.
- Traditional Companies: Established companies may prioritize maintaining existing operations and incremental improvements rather than pushing the boundaries of innovation.
- Risk-Taking and Adaptability:
- Startups: Startups thrive on risk-taking and adaptability. They are willing to embrace uncertainty, pivot when necessary, and iterate on their products or services based on rapid feedback.
- Traditional Companies: Larger, traditional companies may have a more risk-averse culture, as they often have established processes, hierarchies, and a legacy to protect. Change can be slower due to existing structures.
- Focus on Growth Over Profits:
- Startups: Many startups prioritize growth and market share over immediate profitability. They may reinvest earnings to fuel expansion, gain a larger user base, or capture a significant share of the market.
- Traditional Companies: Established companies, especially those publicly traded, often face pressure to deliver consistent profits to shareholders, which may lead to a different approach to resource allocation.
- Lean Operations:
- Startups: Operating with lean resources is a common characteristic of startups. They often seek to maximize efficiency and minimize costs, emphasizing agility and the ability to pivot quickly.
- Traditional Companies: Larger companies may have more extensive resources and established processes, but this can sometimes result in bureaucratic inefficiencies.
- Company Culture:
- Startups: Startup cultures are often characterized by a flat organizational structure, a focus on collaboration, and an emphasis on creativity and individual empowerment.
- Traditional Companies: Larger companies may have more hierarchical structures, defined roles, and established corporate cultures that have evolved over time.
- Speed of Decision-Making:
- Startups: Startups can make decisions quickly due to their smaller size, allowing for rapid iteration and adaptation to changing market conditions.
- Traditional Companies: Decision-making processes in larger companies can be more complex and time-consuming due to hierarchical structures and established protocols.
- Customer-Centric Approach:
- Startups: A strong emphasis on understanding and addressing customer needs is a hallmark of startups. They often prioritize customer feedback and iterate products based on user experiences.
- Traditional Companies: While customer focus is essential for any business, larger companies may face challenges in maintaining the same level of customer intimacy as startups, especially as they scale.
Conclusion: In essence, startups are dynamic entities that thrive on innovation, risk-taking, and a relentless pursuit of growth. Their distinguishing features, including a lean operational approach, emphasis on disruption, and a culture of adaptability, set them apart from traditional companies. While both have their strengths and challenges, understanding the unique characteristics of startups is crucial for entrepreneurs and investors navigating the ever-evolving landscape of the business world. ()